Introduction
Electronic components are the common building blocks of an electronic circuit or electronic system or electronic device. They control the flow of electrons in an electronic system or electronic circuit. Electronic components are very small. Hence, it is easy to carry them from one place to another place. The cost of electronic components is also low. Electronic components contain of two or more terminals. When a group of electronic components is connected together in an electronic board such as printed circuit board (PCB), a useful electronic circuit is formed. Each electronic component in a circuit performs a particular task.
For an excellent electronic analysis, it is necessary to understand how Electronic component work and their uses to make the right choice. Check out this article about the most common Electronic component and how they work.
Electronic Component – Resistor
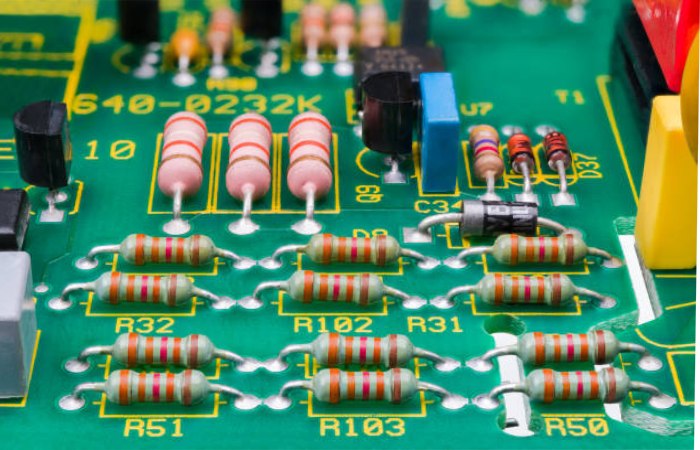
Resistors are electronic component whose primary function is to limit the flow of Electronic charges by converting Electronic energy into thermal energy. Generally, they are made from high-strength dielectric materials, making them capable of reducing the flow of electric current.
Types Of Resistors:
- Thermoresistors: Electronic resistance varies with temperature;
- Photoresistors: vary in Electronic resistance when illuminated;
- Ohmic resistors: they have a fixed resistance.
Electronic Component – Capacitor
Capacitors are devices used to store Electronic charges. When they will connect to a potential difference, an electric field is formed between their plates, causing the capacitors to accumulate amounts at their terminals and the dielectric inside them, making it difficult for electric charges to pass through the leaves.
Capacitors take a short time to charge fully, but they discharge quickly. Therefore, capacitors will be widely used in electronic devices that require large amounts of Electronic current, such as high-power stereos.
In addition to this function, capacitors can implement timers, electric current rectifiers, line filters, stabilizers, etc.
Types of Capacitor:
- Electrolytic capacitors: contain thin layers of aluminum, wrapped in aluminum oxide and soaked in liquid electrolytes.
- Polyester capacitors: a very compact type of capacitor made up of sheets of polyester and aluminum.
- Tantalum capacitors: have a longer lifespan, and Tantalum oxide will use as a dielectric.
- Oil capacitors: These were the first types of capacitors and, like paper capacitors, fell into disuse because they were impractical or unreliable.
- Variable capacitors: these have valves capable of controlling the distance between the plates or their contact areas, widely used in valved devices, such as old radios and televisions.
- Ceramic capacitors: made in the shape of a disk, they will form of conductive plates that surround a medium, such as paper, glass, or air.
Electronic Component – Inductor
Inductors are electronic devices that can store energy through a magnetic field generated by the electric current that flows through it. They will commonly find in electronic circuits, known as coil or solenoids.
Types Of Inductors:
- Air Core: they do not use any material in their Core and have low inductance. However, they do not present losses due to lack of nature and will be widely use in high-frequency circuits.
- Laminated Core: has a core made of layers with thin silicon steel sheets, which are wrapped in varnish and used at low frequencies, as, for example, in transformers. Due to the construction of their Core, laminated inductors have a considerable reduction in losses.
- Ferromagnetic Core: These aim to achieve higher levels of inductance, as they can increase and concentrate the magnetic field. The most significant disadvantage of materials of this type is that many losses occur.
- Ferrite Core: they have an excellent performance when working in circuits of high frequencies and low losses caused by the ferromagnetic and non-conductive ceramic.
- Toroidal inductor: usually constructed of ferrite, it has the shape of a thread. Therefore, its magnetic field has a closed path to circulate, considerably reducing the losses and increasing its inductance value.
Electronic Component – Diode

The diode is a semiconductor electronic component that allows the conduction of electric current in only one direction. If you’ve ever seen an LED panel, you’ve seen thousands of diodes. Each of those little lights in the electronics you have in your home is a type of diode, the light-emitting diode, popularly known as LED.
Types of Diode
LED: uses a chip (similar to the one used in computers), and its function is to transform Electronic current into light.
Photodiode: its primary function is to convert photons into electricity; it acts as a light receptor, which is the opposite of the LED that emits light.
Zener diode: It will obtain modifying the ordinary diode, which is designed to be reverse biased and is also called a reverse conduction diode.
Schottky Diode: uses the Schottky effect, a phenomenon of voltage drop in a semiconductor, which, when forward-biased, has a much lower voltage drop than the ordinary diode.
Rectifier Bridge Diode: the bridge is composed of 4 rectifier diodes united, generally, in a single package and its function is to transform alternating current into direct current.
Tunnel Diode: Its function lets electrons pass freely through barriers in their path.
Varactor diode: it has an essential presence in television circuits and is much smaller than other models. It doesn’t make much noise.
Gunn Diode: Just like the tunnel diode, the Gunn diode also has negative resistance, and its main application is in high-frequency electronic circuits.
Pin diode: not very suitable for rectifier function. It is essential in attenuating circuits and photodetectors that identify gamma- and x-ray photons.
Electronic Component – Transistor
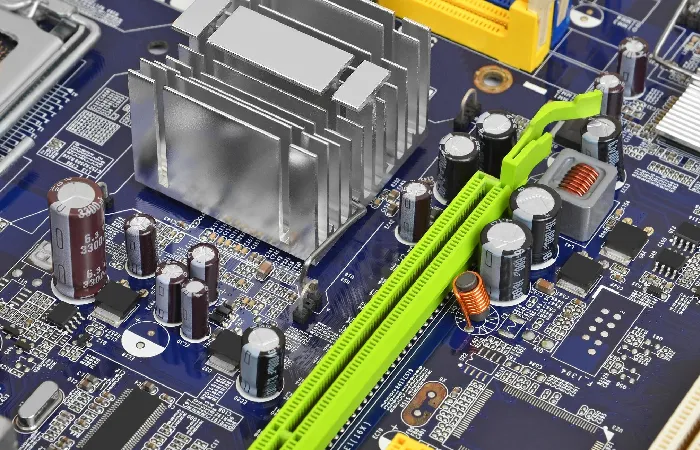
The transistor is a semiconductor device, usually made of silicon or germanium, which amplifies or attenuates the intensity of electric current in electronic circuits. Transistors are like fundamental building blocks in our daily lives, used in computer chips and smartphones, for example.
Transistor Types:
Sandwich: consists of two layers of silicon, one with p-doping and the other with n-doping. It is possible to make electric current flow in only one direction.
Junction transistor: it will form the combination of three silicon layers in different dopings. The appearance of “holes amplifies the electric current.”
Conclusion
Field Effect Transistor (FET) will also form three semiconductor layers, which will activate Electronic voltages and, therefore, can amplify or cancel the Electronic voltage of a circuit. They are cheaper and easier to manufacture than other transistors, widely used in electronic chips.

